CAVA Vision
Compliance with vehicle regulations and requirements for the direct and indirect vision of the driver

Benefits of CAVA Vision
Fulfill Legal Requirements for the Vision of the Driver
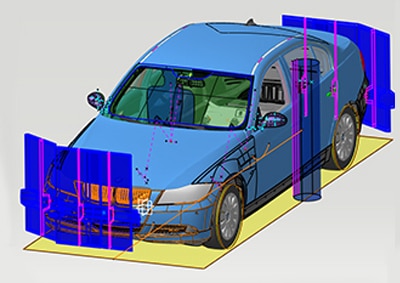
Assess the direct vision of the driver to the front and consider obstructions. Verify the indirect vision through mirrors or a camera-monitor device. Assess the combined vision in close range to the car to detect blind areas. Supports standards from different regions like: UNECE, US FMVSS, GSO, AIS, ADR.
Supports Virtual Homologation of the Rear View Mirror
When compared with a physical test, in most cases the virtual CAVA result is accepted by the certification authorities for the EU standards. Easily modify glass radius parameters, mirror position, driver seat or vehicle loading and get a clear indication of whether a selected standard is fulfilled.
Ergonomic Aspects of Vision and Assisted Driving Support
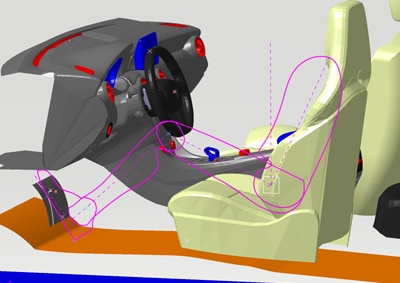
Optimize the comfort and ergonomy of the driver. With CAVA Vision you can assess which areas on the road are visible to the driver, whether the driver would be able to see a traffic light in a given distance, and which areas on the dashboard are obstructed by the steering wheel.
Key Features of CAVA Vision
Analyze Direct Vision of the Driver to the Front
- Calculate the ‘Fields of View’ in the windshield
(UNECE-R 43, FMVSS 104 , ..) - Calculate A- Pillar obstructions (UNECE-R 125)
- Calculate reference points and vision planes
(UNECE-R 125 supp.3) - Analyze optical properties like double angle and optical distortion (UNECE R-43)

Analyze Indirect Vision of the Driver Through Rear View Mirror
- Create the required vision field on the road or on a wall/screen behind the car for the major standards like UNECE-R 46, FMVSS 111
- Automatically creates the eyepoints or eyellipses required by the standard
- Analyze outside and inside mirrors
- Define the mirror parametrically or with help of a mirror surface
- Calculates the required coverage and obstruction values and gives clear indication if the standard is fulfilled
- Also supports mirrors for commercial vehicles: UNECE class II,IV,V,VI and VII

Close Range Vision and Camera Vision
Direct View 3D: Create the obstructed areas on the road or on a wall around a car from the drivers viewpoints. Analyze and detect obstructions from the steering wheel on the dashboard.
Close Range Vision: Detect visibility of cylindrical objects around the car and identify and evaluate blind areas (MLIT 619/2002 Att.81, FMVSS 111, UNECE-R 125). Supports combined direct vision, mirror vision and camera vision.
Camera Fields of View: Calculates the vision cone for a camera and visualizes the visible areas on the road, wall or other objects. Supports user defined vision cones: conical, pyramidal, custom by section or surface. Calculates the combined view of a set of cameras ( like for artificial “surround view”). Applicable for optical cameras but also for similar sensors with a defined vision cone, like ultrasound and thermal imaging and radar as used in aerospace applications.